Documentation
Zapier Consent Database Integration
In this guide, we’ll walk you through Zapier and how to integrate it with iubenda’s Consent Database, and all steps are designed with no programming experience required. To help you find what you’re looking for, please refer to the table of content on the left of the screen.
1. Introduction
What is Zapier
It is frequently described as a translator between online APIs, assisting in increasing worker productivity by saving time by automating regular work and business processes such as lead management. In addition, it orchestrates data flow across tools and online services that would not otherwise connect. This is done via an interface where you can set up workflow rules to govern how its automation function works.
To give an example of this function:
When a new business lead is uploaded to a Google Sheets spreadsheet, the lead may be instantly imported into Salesforce and allocated to a salesperson. Additional team members can be notified via Slack, and the team lead can be notified via email when the new lead is contacted.
Disclaimer
The integration allows for several unique cases, most notably how to handle consent preferences. For example, we have included four different preference options for the “Create a consent” action (newsletter, privacy policy, terms and conditions, and marketing); if you require additional preferences will need to integrate via Webhooks by Zapier and refer to our API HTTP guide. Furthermore, for the time being, all Zapier connection operations will require you to sync their iubenda legal documents with the Consent Database.
2. Start
First, if you haven’t already done so, you need to create an account on Zapier (psst, creating an account is free!). Follow the link below to start your integration process.
Here is your link to start the integration.
Once you have clicked on the link, you will land in the Zapier editor, where you will be prompted to build a Zap with your product.
3. Authentication
Important
If you use Zapier for integrating your Consent Database, make sure you add it to your Privacy Policy.
The Zapier authentication requires you to provide their private iubenda API key, available in the HTTP section of the embedding options for the Consent Database.
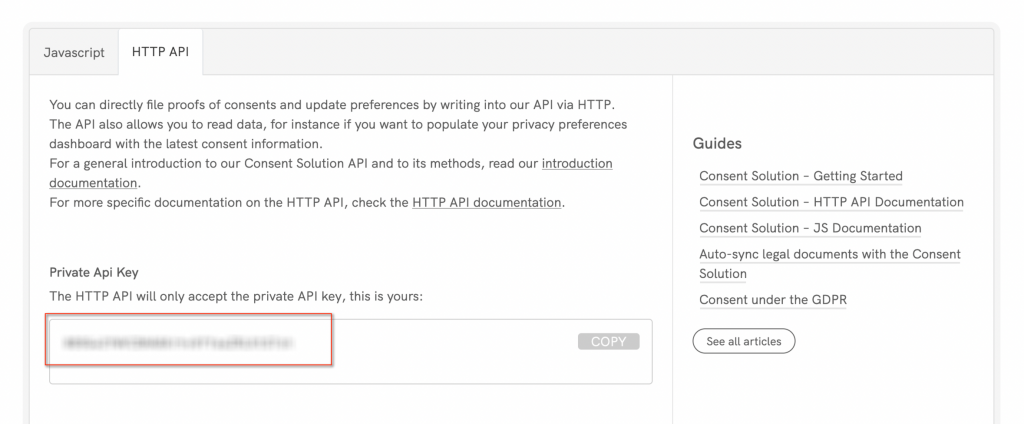
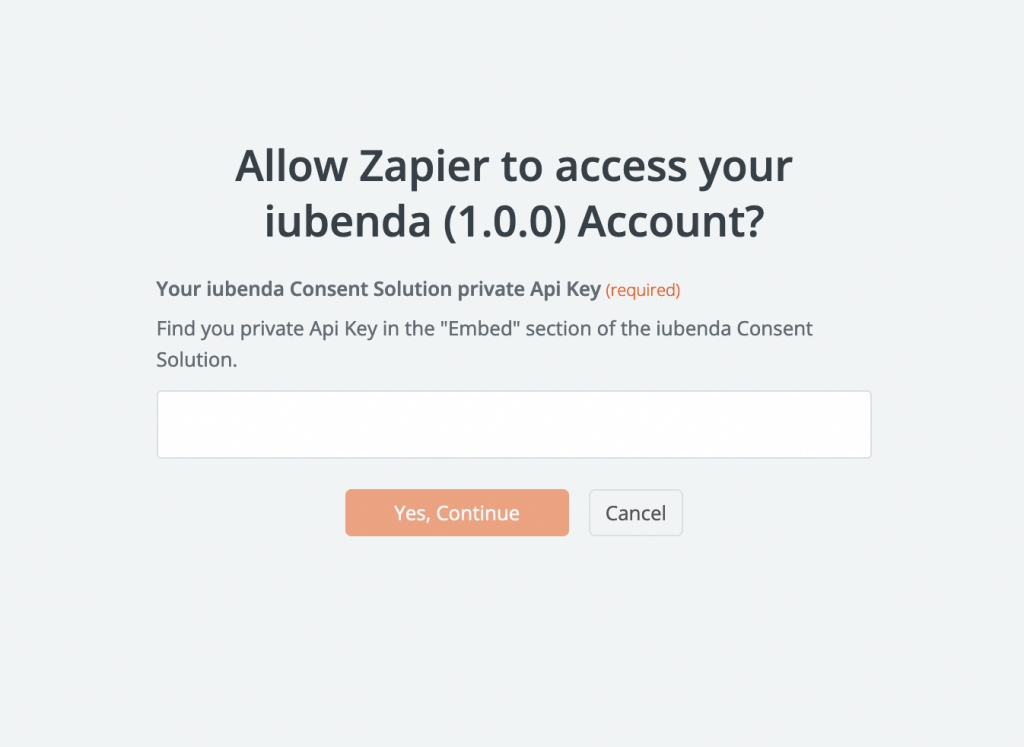
Once you are given Zapier access to the iubenda Consent Database, you’ll be able to connect any other supported service on Zapier as a source for the actions available.
In the following example, a new entry in Typeform would create a new consent in the Consent Database.
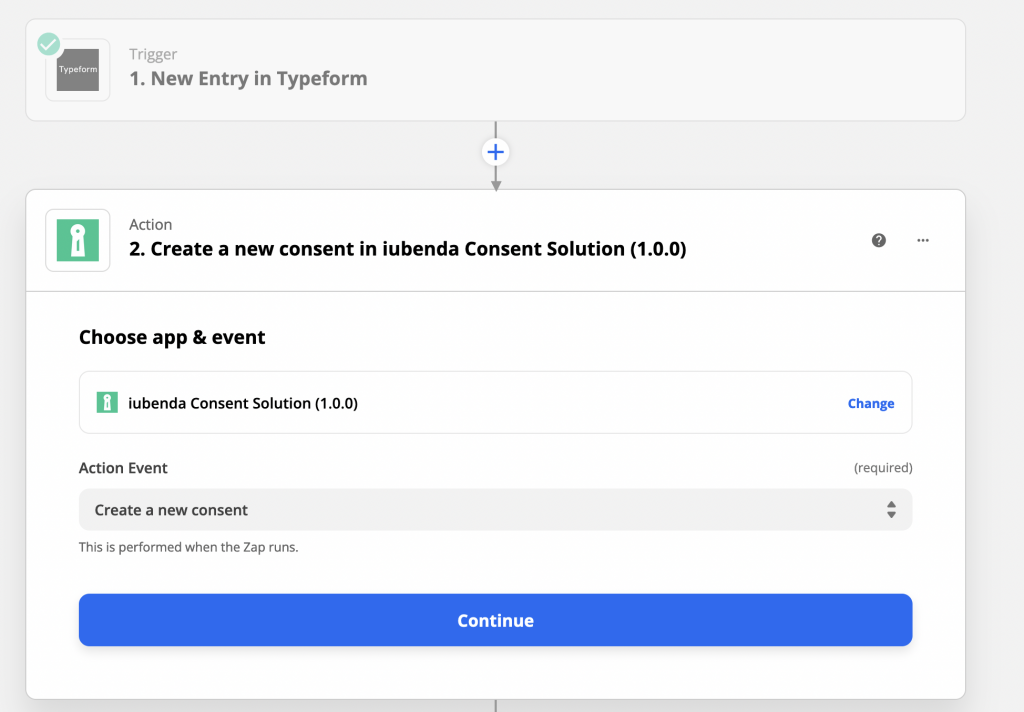
4. Actions available
4.a Create a consent
This action is based on the CREATE consent HTTP request and will create a new consent in the iubenda Consent Database.
The new consent automatically creates a new subject, available in the relative section of the Consent Database dashboard.
Each consent action contains all the information necessary to uniquely identify that specific consent, the subject who performed it, the preferences expressed with that consent, the legal notices the user has accepted, and the proof (e.g., the form the user was presented with).
- Timestamp: if blank, it will be auto-filled
- Subject fields
- Email (required)
- First Name
- Last Name
- Full Name
- Verified (select “True” if users are not verified with double opt-in. If users are identified with double opt-in select “False.” To verify users who double opted-in, you’ll need to create a Zap with the “Verify a subject” action).
- Proofs fields
- Content
- Form (you can put the Form ID or simply an HTML of the form as a static field).
- Preferences fields
- Consent to Privacy Policy (true/false)
- Consent to Newsletter (true/false)
- Consent to Terms and Conditions (true/false)
- Consent to Marketing (true/false)
- IP address
The action also provides three different consent types available for three different use cases:
- Consent to Privacy Policy
- Consent to Newsletter
- Consent to Terms
- Consent to Marketing
If you are not asking for one of these consents, you can leave the relative field blank. Those who want to create additional preferences need to use the HTTP API method.
The output data of the action are:
- Timestamp
- Consent ID
- Subject ID
The data can be used to update the user DB with user-related data (e.g., Subject ID).
4.b Verify a subject
This action is based on the UPDATE subjects HTTP request (with the only verified = “true” attributes in its request body). Use this action to update a subject when verified via the double-opt-in method. This action requires the subject has already been created.
The only field requested is the Subject ID (required).
The action requires that the Subject ID has already been stored by the triggering service. For instance, if you are trying to verify a Mailchimp user who’s just double opted-in, the subject ID must be available in the Mailchimp attributes of the user.
The output data of the action are:
- Timestamp
- Subject ID
4.c Update a subject
This action is based on the UPDATE subjects HTTP request and can be used whenever there’s a need to update a subject (e.g., change in the user’s email address). Keep in mind that if the intent is on changing the user’s preferences, this can be done with the “Update preferences of a subject” action. Blank fields won’t update the previous entry.
- Subject fields
- Subject ID (required)
- First Name
- Last Name
- Full Name
The action requires that the Subject ID has already been stored by the triggering service. For instance, if you are trying to verify a Mailchimp user who’s just double opted-in, the subject ID must be available in the Mailchimp attributes of the user.
The output data of the action are:
- Timestamp
- Subject ID
4.d Update preferences of a subject
This action updates the preferences of a given subject. Any change in preferences requires a new consent; therefore, this action will create a new consent for an existing subject. Information not meant to be updated require the relative fields to be blank.
If you are not asking for one of the preferences consent, you can leave the relative field blank. Those who want to create additional preferences need to use the HTTP API method.
- Subject ID (required)
- Preferences fields
- Consent to Privacy Policy (true/false)
- Consent to Newsletter (true/false)
- Consent to Terms and Conditions (true/false)
- Consent to Marketing (true/false)
If you are not asking for one of the preferences consent, you can leave the relative field blank. Those who want to create additional preferences need to use the HTTP API method.
output data of the action are:
- Timestamp
- Subject ID
5. Example of a Zap
The following Zap will create a new consent in the iubenda Consent Database starting from a new entry on Typeform.
1. First, connect Typeform to Zapier and make it a trigger. Then, select the starting form and test the account. It should pick up the very last entry in the form chosen.
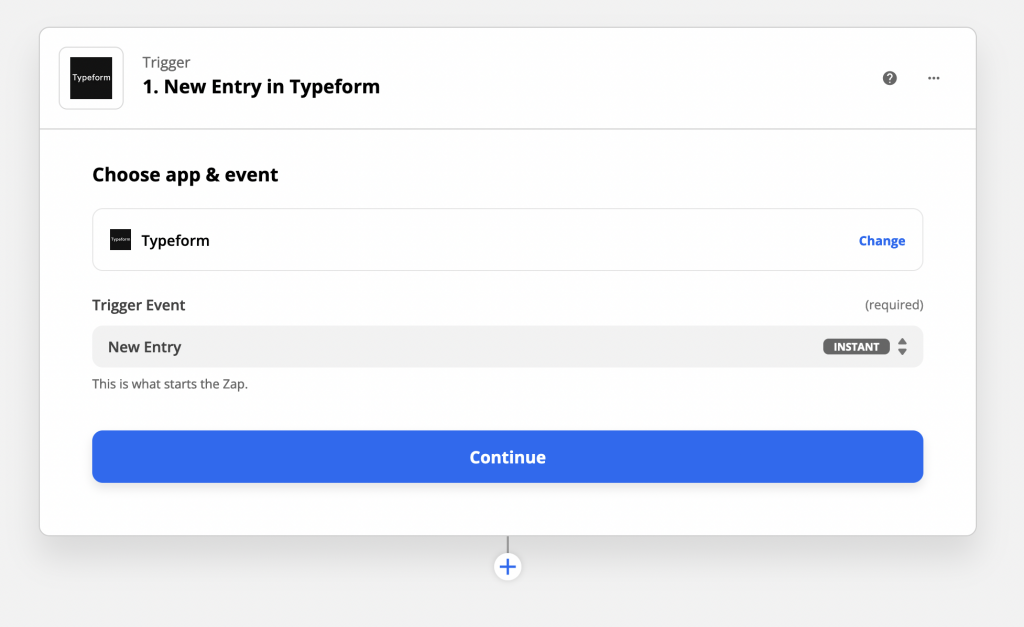
2. After that, click on the + icon and add iubenda as an action in the Zap. Next, select “Create a new consent” in the “Action event” dropdown menu.
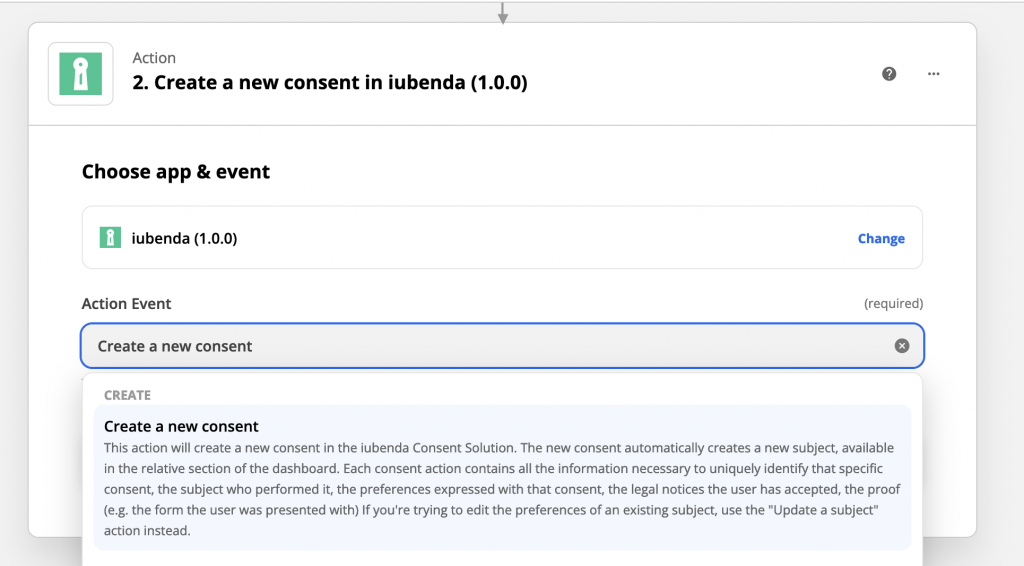
3. Next, connect the iubenda account to Zapier, as described in Authentication.
4. Then, fill the fields with the variables coming from Typeform. Leave blank the fields you don’t need.
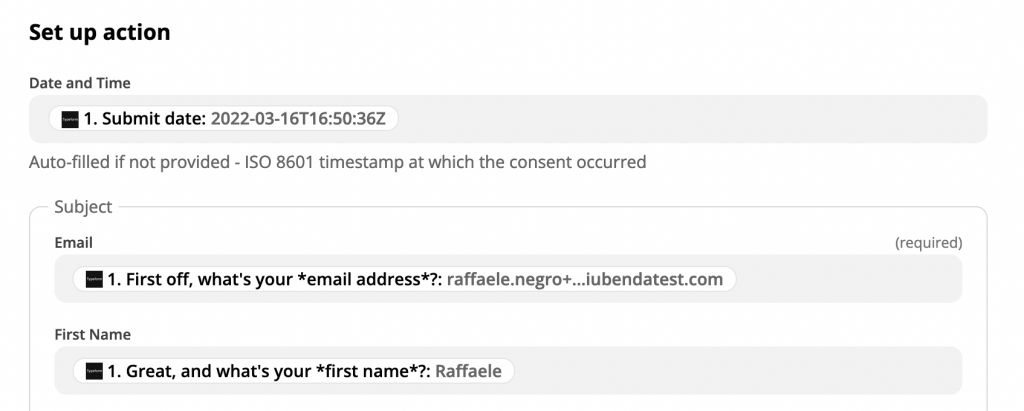
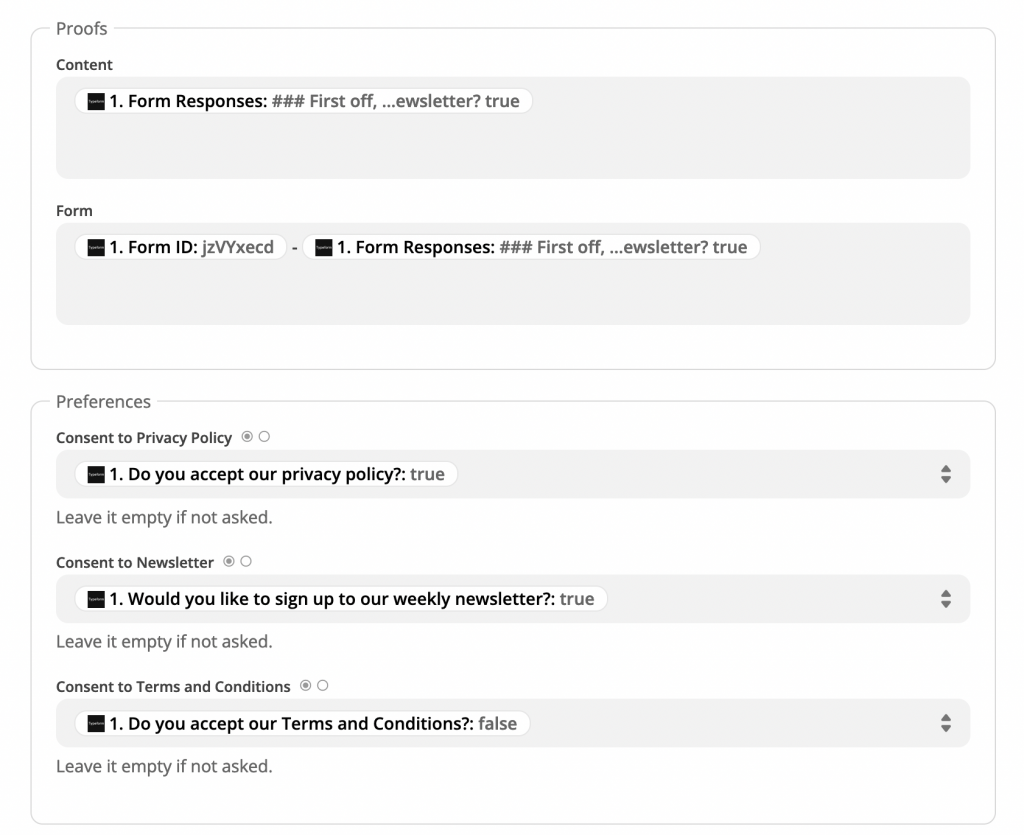
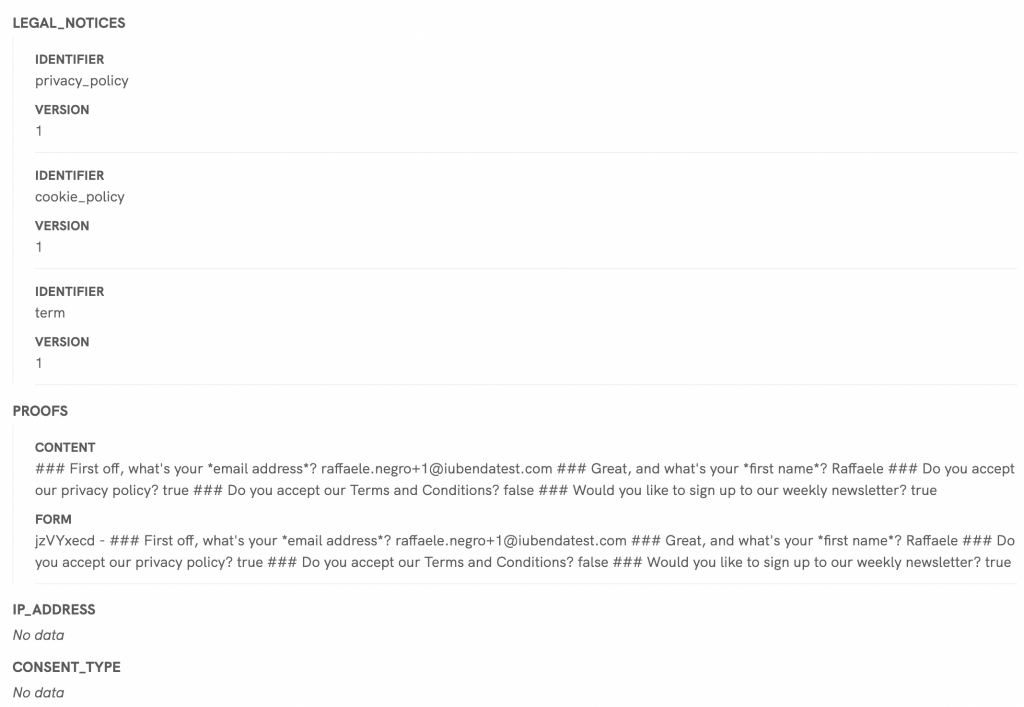
5. Last, click on “Continue,” then “Test and review.” Next, check if the Consent Database dashboard shows the correct information. If yes, turn the Zap on, and you’re done.
6. Most popular Zap templates
There you have it! Now that you went through a crash course on Zapier with iubenda’s Consent Database, here are the most popular Zap templates you can try out, all designed to be no programming experience required:
