Documentation
GDPR Data Mapping Explained and Why It Is Important
If you’re here, you probably want to know more about GDPR data mapping. We’ve got you covered! 👀 In this short post, we look at what data mapping is and why it is so important for GDPR compliance.

🔍 What Is Data Mapping?
Data mapping is a method for keeping track and cataloging all the data you collect, use and store.
👉 It details the types of data and its movements/transfers throughout your business and beyond (for example, data transfer between different departments, to third parties, processors, other countries etc.)
Similar to data mapping, data discovery is a process for putting various sources of data together, sorting the data, analyzing it and organizing it in an easy-to-understand and visual way, in order to get actionable insights. Read our article to learn more.
What Is Data Mapping Under the GDPR?
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requires that both data controllers and data processors keep and maintain “full and extensive” up-to-date records of the particular data processing activities they are carrying out.
In general, records should include:
- The name and contact details of the controller and the processor acting on their behalf, as well as the processor or controller’s representative and DPO, if applicable;
- A description of the various categories of users and data (including from third parties);
- The categories of data recipients, including non-EU third-country recipients or international organizations;
- The purpose of the processing activities;
- Transfers of personal data to a third country and the identification of that third country or international organization, including documentation of suitable safeguards (where applicable);
- Anticipated time limits for erasure of the various categories of data (where possible);
- The technical and organizational security measures described in general terms (where possible).
💡 When are extensive records required?
Full and extensive records of processing are expressly required in cases where the data processing activities:
- are not occasional*; or
- could result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of others; or
- involve the handling of “special categories of data”; or
- is carried out by an organization that has more than 250 employees.
Is Data Mapping Required under GDPR?
The short answer: Yes. Data mapping is a key requirement under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Data mapping involves identifying and documenting the personal data that an organization collects, processes, stores, and shares, as well as the legal basis for doing so.
What Are the Data Mapping Techniques?
There are several data mapping techniques, and you can choose them depending on the complexity of your project. The first one is manual mapping, where you manually match data fields between systems. Then there is automated mapping, which uses tools or software to automatically match data points based on predefined rules. Finally, hybrid mapping combines both methods. It uses automation for some parts, but also lets you oversee the more complex cases manually.
What is a Data Mapping Document?
A data mapping document is a record that shows how data flows between systems and processes. It usually includes information on the source, transformation, and destination of each data element, helping organizations understand how personal data is handled.
For example, a data mapping document may show how customer data collected on a website (source) is transferred to a CRM system (destination), and how it is anonymized (transformation).
How to Create a Data Mapping Sheet?
To create a data mapping sheet, start by identifying all the data sources and destinations within your organization. For each data flow, document the specific data fields involved, the transformations applied (if any), and where the data is stored.
When data activities seem “simple”, it can be tempting to use a regular spreadsheet or make a quick note. However, keeping track of everything (types of data, third parties etc.) can be really complex and this is why we suggest you choose a dedicated tool to build comprehensive and detailed data records (as required by law).
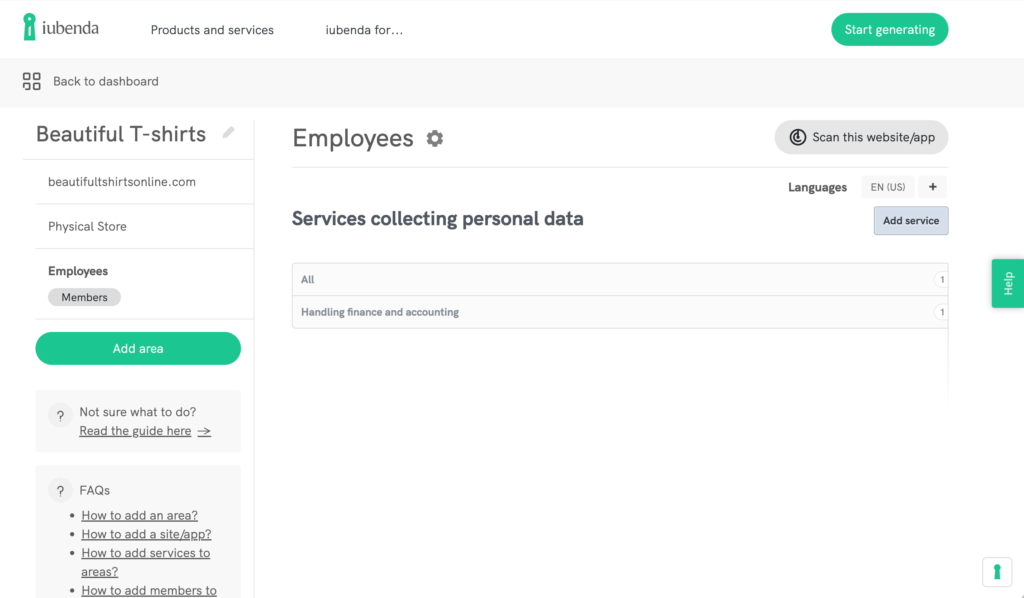
Map your data with iubenda!
Our Record Of Data Processing Activities allows you to record and map the data processing activities within your organization.
Forget about manual mapping! With iubenda, you can add processing activities from 2000+ pre-made options, divide them by area, assign processors and members, and document legal bases and other GDPR-required records.
In this way, you’re always on top of your audits and you can easily create reports of your data processing activities, if needed.
Data Mapping Examples
Now let’s take a look at 3 data mapping examples, to understand how a data map works. The process of mapping doesn’t apply only to compliance with GDPR, but it can be used in many cases – as you will see from a data mapping example below.
🛍️ Customer Data Management
A retail company collects customer names, email addresses, and purchase history through its website. The data is then mapped from the website’s backend to a CRM system, where it’s stored and used for personalized marketing campaigns.
🧑💻 Employee Records
Within a company, personal employee information (such as names, job titles, and salary details) is mapped from an internal database to an HR management software system, ensuring accurate payroll processing and compliance with data protection laws.
📦 Supply Chain Tracking
A logistics company uses data mapping to link order information from its warehouse management system to its inventory system, allowing for real-time tracking and updates on product availability and delivery status. This mapping ensures consistency and accuracy across systems for improved operational efficiency.
🔍 Why Is GDPR Data Mapping So Important?
Of course, apart from meeting one crucial legal requirement of one of the most important privacy laws in the world (the GDPR), data mapping helps organizations to:
- be clear on which data they hold, why and who it is shared with;
- efficiently access and find relevant data whenever required. This is helpful when requests from users arise, i.e. of deleting their personal data. Learn more about users’ rights under the GDPR here;
- identify potential risks to users’ privacy and how to fix them;
- put measures in place for more security and safer practices, where needed.
💡 Data mapping is also a useful tool for DPIAs (Data Protection Impact Assessments):
By conducting a DPIA, you can assess and minimize the risks associated with the processing of personal data. As stated in Article 35 of the GDPR, it is only mandatory when there is a high risk that users’ rights and freedoms could be violated.
👀 Learn more about DPIAs here.
🚀 How iubenda Can Help
Implementing all of the above can be tricky and quite technical.
iubenda’s Register of Data Processing Activities comes in very handy as it greatly simplifies the technical process of creating and maintaining your records of processing activities. Check it out!